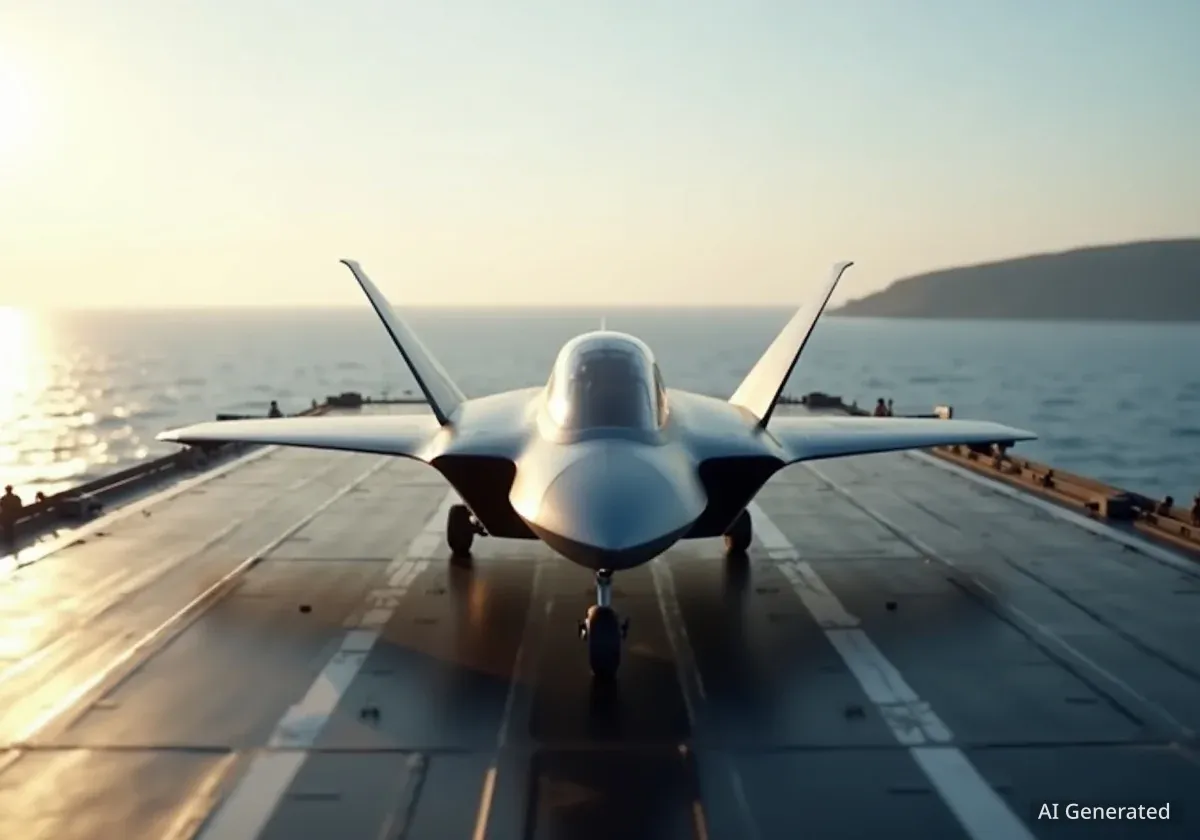
Shield AI has introduced a new multirole fighter jet, the X-BAT, designed to operate without human pilots. This aircraft utilizes the company's Hivemind AI pilot, which previously controlled an F-16 in a simulated dogfight. The X-BAT aims to provide advanced combat capabilities, including the ability to launch from various locations without traditional runways.
Key Takeaways
- Shield AI's X-BAT is a fully autonomous fighter jet.
- It uses the Hivemind AI pilot, tested in an F-16 dogfight.
- The X-BAT can take off from ships and remote islands, not just runways.
- It offers advanced electronic warfare and increased payload capacity.
- The aircraft is designed to be a cost-effective, attritable platform.
Hivemind AI Powers New Autonomous Aircraft
The core technology behind the X-BAT is Shield AI's Hivemind. This artificial intelligence system has a proven track record, notably piloting a modified F-16 in a real-world aerial combat exercise in 2024. During that test, the AI-driven X-62A Variable In-flight Simulation Test Aircraft (VISTA) engaged a crewed fighter jet.
Armor Harris, Shield AI's senior vice president of aircraft engineering, confirmed that Hivemind is the same combat-proven AI pilot used in the F-16 dogfight. This marks a significant step from experimental AI in existing platforms to a purpose-built autonomous aircraft.
AI Dogfight Landmark
In 2024, the Hivemind AI successfully piloted a modified F-16 (X-62A VISTA) in a dogfight against a human-crewed fighter. Former Air Force Secretary Frank Kendall was on board the AI-driven aircraft during this test, calling it a "transformational moment" for autonomous air-to-air combat.
Flexible Deployment from Remote Locations
A key feature of the X-BAT is its operational flexibility. Shield AI states the jet can take off and land vertically, eliminating the need for long runways. This capability allows it to launch from a variety of unconventional locations, including container ships, remote islands, and austere forward operating sites.
The aircraft boasts a 2,000-nautical-mile range. This extended reach, combined with its vertical takeoff and landing (VTOL) ability, could be crucial for operations in vast geographical areas. The Indo-Pacific region, characterized by large bodies of water and dispersed landmasses, is one area where such capabilities could be particularly valuable.
"X-BAT frees human aviators for missions that demand critical human judgment — an essential advantage in today's fast-moving and unpredictable conflict zones," Shield AI stated.
Overcoming Geographic Challenges
The ability to deploy from almost anywhere provides commanders with unprecedented power to project combat airpower. Harris noted that large amphibious warships could host up to 60 X-BATs. Even typical container ships could serve as launch platforms, expanding strategic options.
This design is unique in its class for combining vertical takeoff and landing with such an extensive range. It positions the X-BAT as a versatile asset for various military branches, including the US Navy, Air Force, Marine Corps, and Army, as well as allied forces.
Role in Collaborative Combat Aircraft Programs
The US Air Force has shown significant interest in autonomous uncrewed assets through its Collaborative Combat Aircraft (CCA) program. These CCAs are designed to fly alongside crewed fighter jets, acting as drone wingmen to enhance protection and expand overall combat power.
Shield AI designed the X-BAT to go beyond the initial Increment 1 phase of CCA development. This next-generation aircraft features advanced electronic warfare capabilities, greater payload capacity, and extended range. These enhancements aim to provide combatant commanders with geographically distributed long-range fires and effects, an area where the military acknowledges a need for advancement.
Collaborative Combat Aircraft (CCA)
The CCA program focuses on developing affordable, attritable warfighting platforms. These uncrewed aircraft can support and, if necessary, be sacrificed for more expensive crewed fighters. This strategy aims to create a larger, more resilient fleet capable of withstanding losses in high-intensity conflicts without severe pilot casualties or prohibitive financial costs.
Affordability and Future Warfare
A significant advantage of the X-BAT is its cost-effectiveness. Shield AI highlights that the new design delivers high-end capabilities for a fraction of the cost of traditional fighter jets. This affordability is central to the concept of attritable warfighting platforms.
Filling military fleets with such aircraft can lead to a larger and more resilient force. This approach allows for absorbing hits without severe pilot losses or budget-breaking aircraft replacements, which is critical for peer-level combat scenarios.
- Reduced Costs: X-BAT is significantly cheaper than conventional fighter jets.
- Increased Resilience: Allows for a larger, more distributed fleet.
- Pilot Safety: Eliminates risk to human pilots in dangerous missions.
- Strategic Advantage: Reshapes how future conflicts are fought and sustained.
Frank Kendall, the former Air Force secretary, stated that the "AI competition is essentially going to determine who's the winner in the next battlefield." He views the F-16 dogfight as a pivotal moment, transforming autonomous air-to-air combat from a distant dream into a tangible reality.
The X-BAT was unveiled in Washington, DC, to military leaders and politicians. While its exact role in future US or allied military operations is still being determined, the growing interest in autonomous systems suggests a shift in defense strategies. Other defense companies, like Airbus, are also exploring AI integration, with Shield AI's Hivemind already tested on aircraft such as the H145 helicopter.