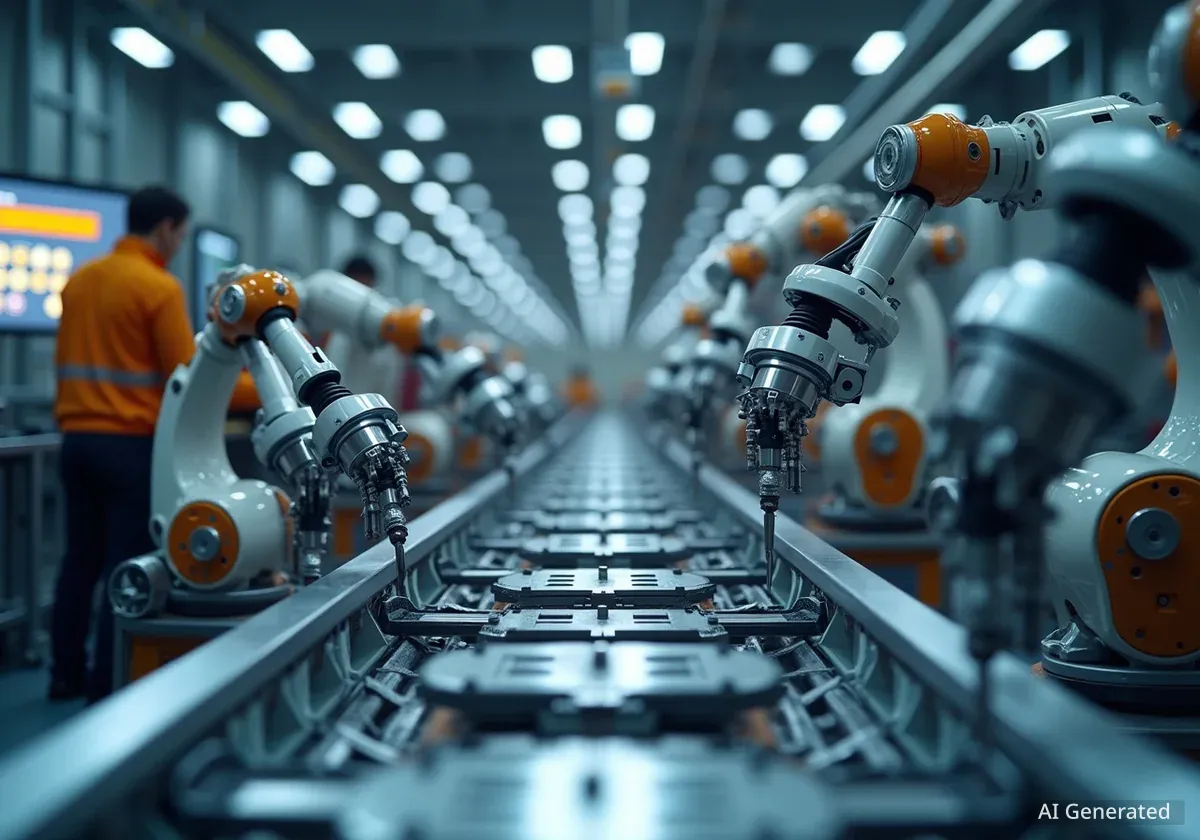
The traditional image of a factory, a place of loud machinery and manual labor, is undergoing a significant transformation. Modern manufacturing is increasingly integrating advanced digital technologies, moving beyond simple automation to create intelligent, interconnected production systems. This shift is reshaping how goods are made, from raw materials to finished products, impacting efficiency, quality, and the nature of work itself.
Key Takeaways
- Modern factories use digital tools to optimize production.
- Technology enables real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance.
- The definition of a 'factory' is expanding beyond physical walls.
The Evolving Landscape of Production
For decades, a factory's operations were defined by its physical footprint and the manual processes within its walls. Ross McGregor, who runs Pentaflex, a manufacturing business founded by his father over 50 years ago in Springfield, Ohio, describes the intricate coordination of his roughly 80 employees. They transform raw steel into products like commercial truck brake systems, often completing the entire process within a single week.
This traditional model emphasizes a synchronized workflow, a "symphony" of human effort and machinery. While such efficiency remains crucial, digital integration is adding new layers of precision and control. The goal is to enhance this symphony with data-driven insights, making operations even more fluid and responsive.
Fact: Digital Integration
Many modern manufacturing facilities are now incorporating IoT sensors, AI-powered analytics, and advanced robotics to streamline production processes and improve decision-making.
From Manual to Smart Operations
The core function of a factory—taking raw materials and turning them into finished goods—remains constant. However, the methods employed are changing dramatically. Digital tools are moving beyond automating repetitive tasks. They are enabling complex data analysis, predictive maintenance, and real-time adjustments to production lines.
This means that while human skill and oversight are still vital, they are increasingly augmented by intelligent systems. These systems can monitor machine performance, identify potential issues before they cause downtime, and optimize material flow, leading to significant improvements in overall output and resource utilization.
"The future of manufacturing lies not just in what we produce, but how intelligently we produce it. Data is becoming as valuable as raw materials."
The Role of Data and Connectivity
Connectivity is a cornerstone of this modern factory. Machines are no longer isolated units; they communicate with each other and with central control systems. This network allows for a holistic view of the production process, enabling managers to identify bottlenecks, optimize schedules, and ensure quality at every stage.
For example, sensors on a welding robot can send data about its performance, alerting technicians to calibration needs before the weld quality degrades. Similarly, inventory management systems can automatically reorder materials based on real-time consumption rates, preventing costly delays.
Context: Industry 4.0
The term Industry 4.0 describes the current trend of automation and data exchange in manufacturing technologies. It includes cyber-physical systems, the Internet of Things (IoT), cloud computing, and cognitive computing. This concept is driving the shift towards smart factories.
Impact on Workforce and Skills
The integration of digital technologies also has a profound impact on the workforce. While some fear job displacement, many experts believe it creates a need for new skills and roles. Employees in modern factories are increasingly involved in monitoring systems, analyzing data, and troubleshooting complex automated processes.
This shift requires workers to possess a blend of traditional mechanical skills and digital literacy. Training programs are adapting to equip the workforce with the knowledge needed to operate and manage these advanced systems, ensuring that human expertise remains central to manufacturing success.
- Enhanced Efficiency: Digital tools reduce waste and optimize production cycles.
- Improved Quality: Real-time monitoring helps maintain consistent product standards.
- Greater Flexibility: Automated systems can adapt more quickly to changes in demand.
- Safer Workplaces: Robots can handle dangerous or repetitive tasks, reducing human risk.
Beyond the Factory Floor
The influence of digital transformation extends beyond the factory floor itself. Supply chains are becoming more transparent and responsive through digital tracking and communication. This allows for better coordination with suppliers and distributors, reducing lead times and improving overall market responsiveness.
Customers also benefit from this digital evolution. Personalized products, faster delivery, and higher quality goods are all outcomes of more efficient and intelligent manufacturing processes. The ability to quickly adapt to market demands and innovate new products is becoming a key competitive advantage.
The transformation of manufacturing is not a sudden revolution but an ongoing evolution. It combines the foundational principles of efficient production with the cutting-edge capabilities of digital technology, creating a future where factories are not just places of production, but hubs of innovation and data-driven intelligence.